-
+98 9194451528
-
info@granuleplus.com
Professional plastic raw materials
The plastic industry, while facing mounting environmental concerns, has embraced the use of recycled raw materials as a key solution for a more sustainable future. Professional plastic raw materials are high-quality, specialty materials used in various industries for manufacturing diverse products. These materials undergo rigorous testing and quality control procedures to ensure they meet industry standards and perform consistently in various applications. Granuleplus company known as a professional Recycled Plastic Raw Materials Supplier and manufacturer in Asia . In this article we will get to know Recycled Raw Materials for Plastic Industry Used. Contact us if you have any inquiry or requests.
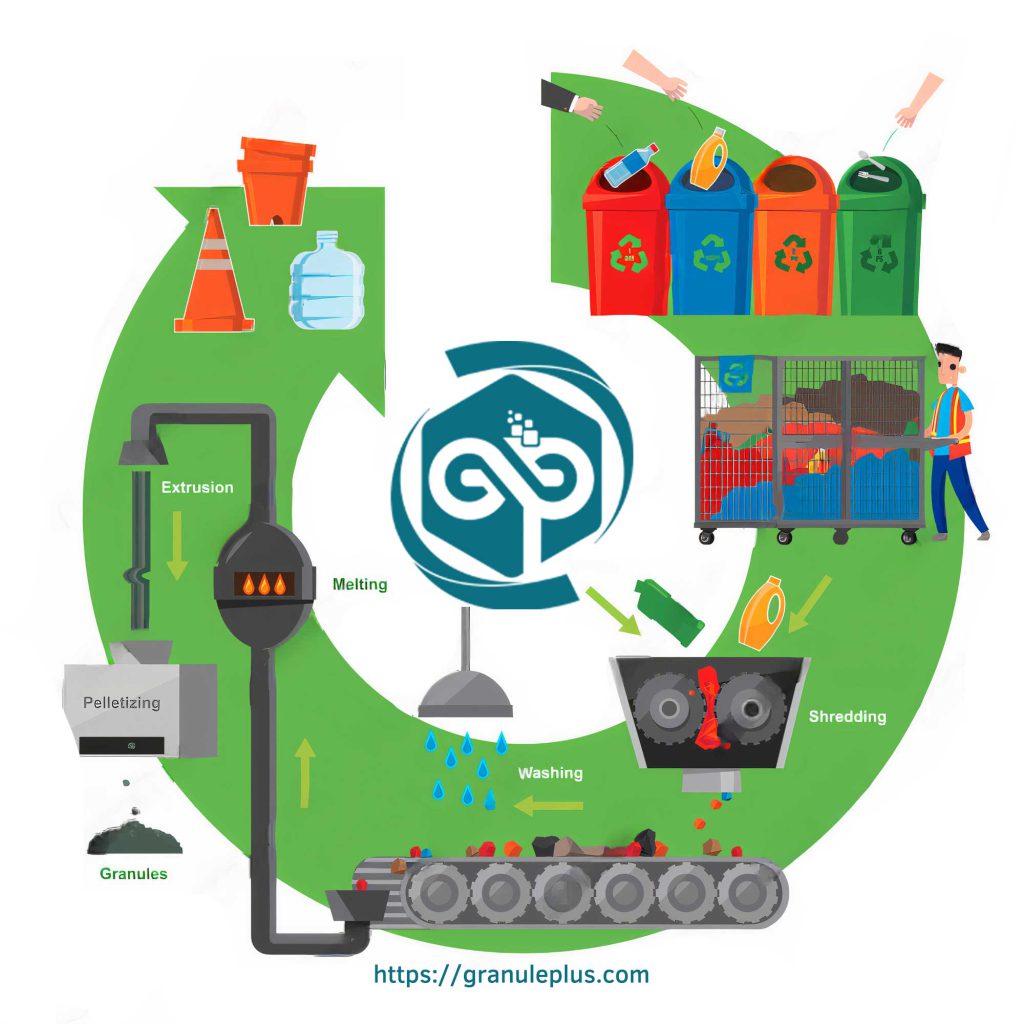
Recycled Raw Materials for Plastic Industry Used
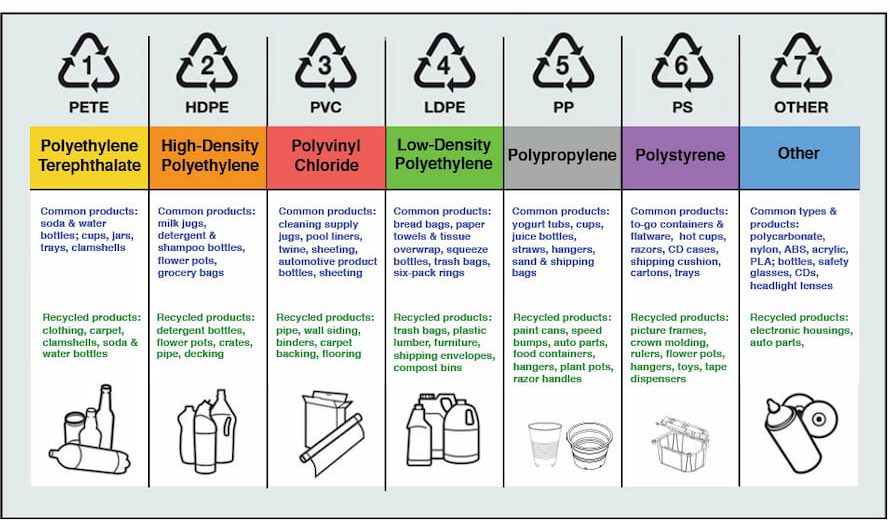
Recycled Plastic Types
PET (Polyethylene terephthalate): Primarily used in beverage bottles, food packaging, and textiles. High recycling rate and versatility make it a popular choice for new bottles, clothing fibers, and packaging materials.
HDPE (High-density polyethylene): Common in milk jugs, detergent bottles, and pipes. Its durability makes it suitable for outdoor furniture, construction materials, and flooring.
LDPE (Low-density polyethylene): Found in grocery bags, trash bags, and squeezable bottles. Often recycled into new bags, pipes, and agricultural mulch.
PP (Polypropylene): Used in yogurt containers, straws, and car parts. Offers good heat resistance, making it suitable for automotive parts, appliances, and medical equipment.
PVC (Polyvinyl chloride): Used in pipes, flooring, and window frames. Can be recycled into new pipes, construction materials, and decking.
Other polymers: PS (polystyrene), PC (polycarbonate), and ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) are also recycled, though in smaller quantities, for specific applications.

Key Characteristics
- Consistency and Reliability: Professional plastic raw materials exhibit consistent properties and performance, ensuring predictability and reliability in manufacturing processes. This consistency is crucial for achieving desired product quality and performance.
- High Performance: These materials are designed to meet specific performance requirements, such as high strength, impact resistance, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. They are tailored for specific applications and provide the necessary properties for optimal product performance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Professional plastic raw materials adhere to stringent regulatory standards, ensuring product safety and compliance with environmental regulations. This compliance is essential for consumer protection and environmental responsibility.
- Traceability: Professional suppliers maintain traceability of their raw materials, allowing for identification of the material’s origin and manufacturing process. This traceability facilitates quality control and ensures product integrity.
- Technical Support: Suppliers of professional plastic raw materials provide technical support to assist customers in selecting the appropriate materials, optimizing processing parameters, and troubleshooting any issues. This support ensures efficient and effective utilization of the materials.
Industries Using
- Automotive Industry: These materials are used for manufacturing car parts, interior components, and exterior trim. They require high impact resistance, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
- Packaging Industry: Plastic raw materials are widely used in food packaging, beverage packaging, and consumer goods packaging. They need to meet food safety standards, provide barrier properties, and offer recyclability.
- Electronics Industry: Plastic raw materials are used in electronic components, enclosures, and cable insulation. They require electrical insulation properties, flame retardancy, and dimensional stability.
- Medical Industry: Medical-grade plastic raw materials are used for manufacturing medical devices, implants, and packaging. They must meet strict biocompatibility standards, sterility requirements, and regulatory compliance.
- Construction Industry: Plastic raw materials are used in building materials, pipes, and fittings. They require high strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors.


Benefits of Using Recycled Raw Materials
Reduces reliance on virgin fossil fuels: Extracting and processing virgin materials is energy-intensive and depletes finite resources. Recycled plastic significantly cuts down on this.
Decreases landfill waste: Plastic pollution is a major global issue. Recycling diverts plastic waste from landfills, protecting ecosystems and human health.
Lower greenhouse gas emissions: Recycling generates fewer emissions compared to virgin plastic production, contributing to climate change mitigation.
Economic benefits: Creates jobs in the recycling and remanufacturing sectors, stimulating economic growth.
Challenges of plastic recycling
Sorting and contamination: Different types of plastics require separate processing, and contamination with non-plastics or incompatible plastic types can compromise quality.
Quality concerns: Recycled plastic can sometimes have lower strength or performance compared to virgin materials, limiting its applications.
Technological and economic barriers: Advanced technologies and efficient collection systems are needed for broader adoption and cost-competitiveness.
So recycled raw materials play a crucial role in building a more sustainable plastic industry. Overcoming challenges and improving technologies will further unlock the potential of recycling and contribute to a circular economy for plastics.

Examples of Professional Plastic Raw Materials
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Used in food and beverage packaging, textiles, and engineering applications.
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): Used in bottles, containers, pipes, and industrial applications.
- Polypropylene (PP): Used in packaging, textiles, automotive parts, and appliances.
- Polystyrene (PS): Used in disposable packaging, toys, and electronics casings.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Used in pipes, fittings, windows, and flooring.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Used in automotive parts, appliances, and electronics casings.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Used in safety glasses, medical devices, and impact-resistant applications.
- Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA): Used in acrylic sheets, lenses, and displays.
- Polyurethane (PU): Used in foams, adhesives, and coatings.
- Nylon: Used in textiles, engineering components, and fibers.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of professional plastic raw materials available, each with its unique properties and applications. The selection of the appropriate material depends on the specific requirements of the product and the manufacturing process.
- WhatsApp: +989194451528
- info@granuleplus.com
- trelegram: granulplus
- granulplus
